CD3, The Golden Target for TCE Bispecific and Multi-specific Antibodies
Novoprotein 2024 Linkedin
Following ADCs and nucleic acid drugs, the research focus has now shifted to TCE (T cell engager) drugs. T cell redirecting bispecific antibodies (TCE) can simultaneously bind to tumor-associated antigens and the CD3 molecule on T cells, thereby linking T cells with tumor cells and activating T cells to exert anti-tumor effects. This therapy has been successfully applied in the treatment of various hematologic tumors. In the field of autoimmune diseases, TCE is also an innovative therapeutic antibody that can recruit T cells to the affected area to eliminate overactive autoimmune cells.
With the expanding market for bispecific antibodies, CD3-targeted drugs are showing strong growth, with over 300 companies involved both domestically and internationally, and numerous significant business development deals. On August 9, Merck introduced the CD3/CD19 bispecific antibody CN201 from Tongrun Biotech for $1.3 billion. On September 4, Vignette Bio acquired the CD3/BCMA bispecific antibody EMB-06 from Anmai Biotech for over $600 million. On November 17, Keymed Biosciences Inc. licensed the BCMA/CD3 bispecific antibody CM336, worth up to $626 million. In addition to major deals targeting hematologic cancers, the potential of CD3-TCE in autoimmune diseases is also gradually being confirmed in clinical research.
In April 2024, Nature Medicine published preliminary research showing positive results for Amgen's CD3/CD19 bispecific antibody Blinatumomab in patients with multidrug-resistant rheumatoid arthritis. In September 2024, clinical studies published in The New England Journal of Medicine demonstrated significant efficacy of Johnson & Johnson's CD3/BCMA bispecific antibody Teclistamab in patients with severe systemic lupus erythematosus.
| Cat. No. | Product Name |
| C578 | Human CD3E(C-6His) |
| CP19 | Human CD3E(C-Fc) |
| C00E | Human CD3E(C-mFc) |
| CY33 | Biotinylated Human CD3E (C-Fc-Avi) |
| CW07 | Cynomolgus CD3E(C-Fc) |
| C03Y | Human CD3D&CD3E Heterodimer (C-Fc-Flag&C-Fc-6His) |
| C33F | Human CD3D&CD3E Heterodimer V2 (C-6His) |
| C09K | Cynomolgus CD3D&CD3E Heterodimer (C-Fc-Flag&C-Fc-6His) |
| C08G | Human CD3E&CD3G Heterodimer (C-Fc-6His&C-Fc-Flag) |
| C577 | Human CD3D (C-6His) |
| CS63 | Cynomolgus CD3d (C-6His) |
| C897 | Human MAG (C-6His) |
| Cat. No. | Product Name |
| C565 | Human MOG (C-6His) |
| CF66-A | Human monomeric alpha-Synuclein(Ultra-low Endotoxin) |
| CF66 | Human monomeric alpha-Synuclein |
| CH45 | Human SNCA (N-6His) {Human Alpha-Synuclein } |
| CM23 | Mouse SNCA {Mouse Alpha-Synuclein} |
| CK23 | Mouse SNCA (N-6His) {Mouse Alpha-Synuclein} |
| CJ40 | Human IL-23 (C-6His) |
| C03U | Human IL-23 |
| C091 | Human IL-33 |
| CG73 | Mouse IL-33 |
| CR61 | Human IL-36 alpha |
| CR57 | Human IL-36 Beta(157AA) |
| CM77 | Human IL-36 gamma |
In the layout of bispecific antibodies, CD3 is undoubtedly the "core target." In addition to classic pairings like CD3×CD19, CD3×CD20, and CD3×BCMA, more target combinations are under development. According to statistics from the PharmaSeek database, there are currently 417 CD3-related drugs in development, of which 409 are antibody drugs, with 378 being mult-ispecific and 333 being bispecific. As of now, there are 12 approved CD3-targeted drugs, 10 of which are bispecific antibodies.
Table 1: Summary of CD3-TCE Approved Drugs (Source: PharmaSeek)
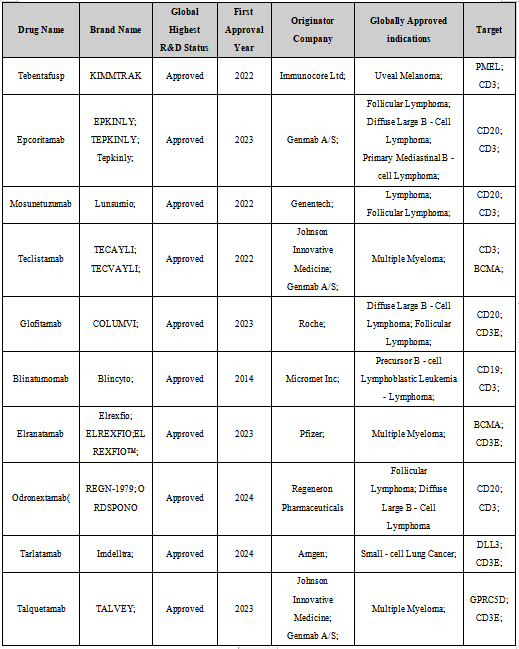
CD3 is a polymeric protein complex consisting of four polypeptide chains: epsilon (ε), gamma (γ), delta (δ), and zeta (ζ). CD3ε, CD3δ, CD3γ, and CD3ζ are encoded by the CD3E, CD3D, CD3G, and CD247 genes, respectively. This forms three distinct subunits: CD3δε, CD3γε, and CD3ζπ dimers. The cytoplasmic tails of CD3ε, CD3δ, and CD3γ each contain an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM), while the cytoplasmic tail of CD3ζ contains three ITAMs. As a result, a CD3 complex contains 10 ITAMs, making it highly sensitive to antigen binding.

Figure 2: Schematic Diagram of CD3 Structure
After the CD3 subunits bind to the α and β chains of the T cell receptor (TCR), they form a complete TCR–CD3 complex, which functions as a full functional unit: providing the "first signal" to initiate T cell activation and determining the specificity of the immune response. The TCR provides binding specificity, while the CD3 subunits facilitate the necessary signaling for T cell activation. The TCRαβ recognizes the pMHC complex on antigen-presenting cells at the immunological synapse, and the ITAM domains in the intracellular regions of the CD3 subunits mediate signal transduction. These domains are phosphorylated by Src family kinases. The cascade reaction ultimately leads to the production of second messengers (Ca2+, diacylglycerol (DAG), and IP3) and activation of Ras, which, through NF-κB, AP-1, and NFAT, triggers the upregulation of gene transcription and initiates T cell activation.
The transmembrane regions of all CD3 subunits and TCR chains tightly bind to each other through complementary electrostatic interactions between amino acid residues with opposite charges. This complementary electrostatic organization causes the transmembrane helices of each TCR/CD3 subunit to intertwine, anchoring the TCR/CD3 complex firmly in the cell membrane and allowing it to move as a single, independent functional unit within the lipid bilayer. As a key regulatory node in T cell immune responses, CD3 plays a critical role in modulating T cell activation and the strength of the immune response. Intervening with the CD3 target is significant in the treatment of immune diseases and cancer immunotherapy.
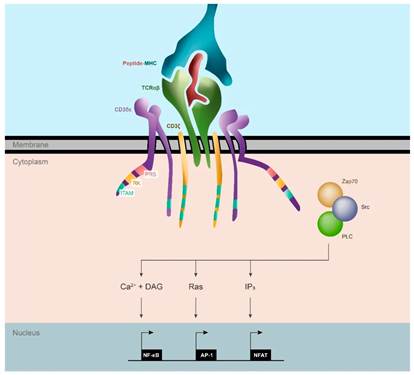
Figure 3: TCR Structure and T Cell Activation Pathway
Due to its unique structural functions, the CD3 target remains a key focus in antibody research and development worldwide, despite challenges such as cytokine release syndrome (CRS), low efficiency, and treatment resistance. Pharmaceutical companies are actively exploring breakthroughs, and with the extensive clinical development of CD3 drugs, there is hope that more CD3-targeted therapies will emerge as "beacons of treatment" and reach the market.
Novoprotein provides a range of CD3-targeted antigens and a variety of tumor targets, suitable for the development of bispecific and multispecific antibody drugs. Additionally, CD3-TCE has shown positive effects in autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis by regulating T cell activity and immune tolerance mechanisms.
Novoprotein currently offers MOG protein, which can be used for experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) animal modeling, assisting in the evaluation of the efficacy of related CD3-TCE drugs.
Furthermore, Novoprotein provides reference antibodies validated by ELISA/BLI, which can be used as positive controls in antibody drug development and in basic scientific research.
CD3 Target: Data Display
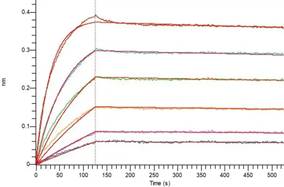
Loaded Anti-Human CD3E mAb-mFc(NC079) on AMC Biosensor, can bind Human CD3E-Fc-6His&C-Fc-Flag(CY33) with an affinity constant of 0.6 nM as determined in BLI assay.
%20on%20Protein%20A%20Biosensor.png)
Loaded Anti-Human/Monkey CD3E mAb-Fc(NC006) on Protein A Biosensor, can bind Human CD3D&CD3E Heterodimer-His(C01S) with an affinity constant of 1.13 nM as determined in BLI assay.
